Today is the day! — Nitrux 2.6.0 “ff” is available to download
We are pleased to announce the launch of Nitrux 2.6.0. This new version combines the latest software updates, bug fixes, performance improvements, and ready-to-use hardware support.
Nitrux 2.6.0 is available immediately.
📜 Table of Contents
✨ What’s new
We recommend new users do a fresh installation using the latest media. For users of the previous version (2.5.1), please check the Notes.
- See Notes for detailed information on a list of packages updated from the last release.
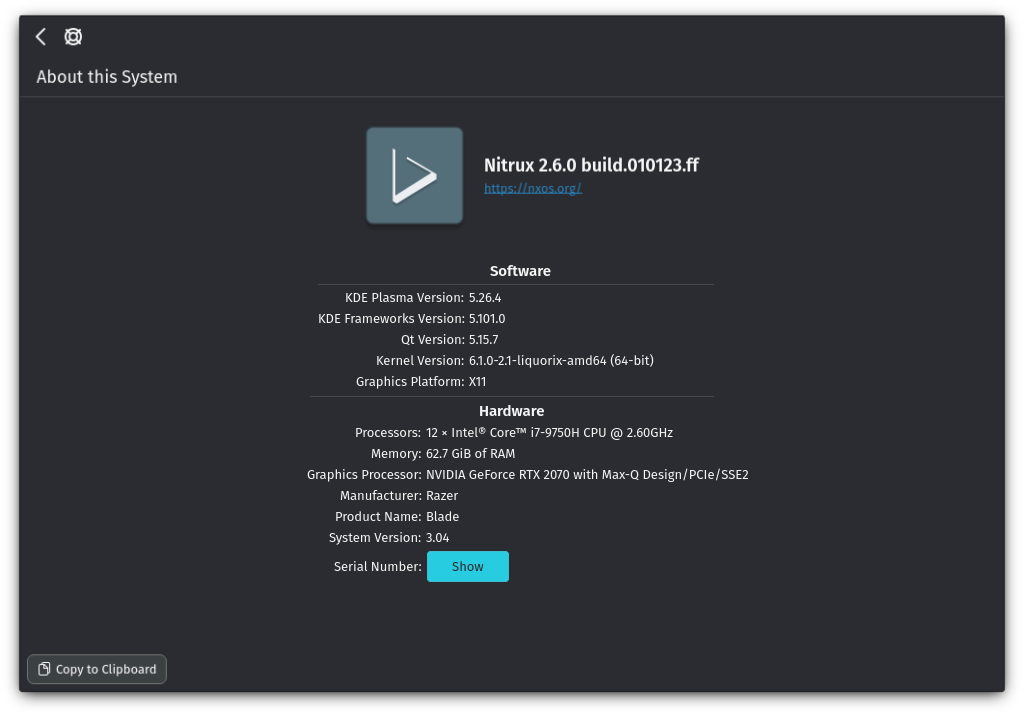
The 6.1.0-2.1 Liquorix kernel is now the default in the distribution.
We’ve updated the following components of the distribution. For other information, see Notes.
- KDE Plasma to version 5.26.4, KDE Frameworks to version 5.101.0, and KDE Gear to version 22.12.0.
- Firefox to version 108.0.1.
- We’ve updated MESA to version 23.0~git2301020600.fc0e23~oibaf~l.
- Disclaimer: We do not develop or package MESA. To file bugs against MESA, please use their bug tracker here.
- We’ve added PipeWire and Wayland by default.
- Plasma (Wayland) is available to select from SDDM.
- ⚠️ Important: If using an Nvidia GPU, check the KDE Wiki instructions here to use the Plasma (Wayland) session, YMMV.
- Disclaimer: We do not develop KWin, Wayland, Plasma Wayland, or the Nvidia proprietary driver. For the best experience using the Plasma (Wayland) session, use a Linux-friendly GPU and driver such as Intel or AMD.
- The Plasma (Wayland) session is not the default; the Plasma (X11) session is still the default.
- ⚠️ Important: If using an Nvidia GPU, check the KDE Wiki instructions here to use the Plasma (Wayland) session, YMMV.
- When logging in, you may hear a “pop” sound; this is not a bug; it is a test to ensure that PipeWire is working; you may replace the file used for this test. The file can be found at “$HOME/.local/share/sounds/pop1.wav”
- Plasma (Wayland) is available to select from SDDM.
- We’ve enabled Flathub by default.
- To enable Flathub-beta, see Notes.
- We’ve added Samba.
- We’ve set the state of the root directory to be immutable using overlayroot.
- This change allows us to provide new versions of the distribution with a higher degree of certainty that no changes have occurred to the root that might cause a conflict down the line.
- And also to avoid sudden issues from upgraded packages coming from a different origin than our repository, which we have a minimal way of controlling.
- So, please check for detailed and updated instructions in the Notes to perform distribution upgrades.
- We’ve updated our settings for Calamares to do the following.
- Calamares now creates a custom layout when selecting the option “Erase disk.” This layout is intended to accommodate the new update process; the default option, however, continues to be “Manual partitioning.”
- The layout assigns the partition size in percentages, 20% for the root (label: NX_ROOTD), 60% for the home (label: NX_HOMED), and 10% for two partitions /var/lib/flatpak and /Applications (label: NX_SYSFLTPK and NX_SYSAPPIM, respectively.)
- Calamares now creates a custom layout when selecting the option “Erase disk.” This layout is intended to accommodate the new update process; the default option, however, continues to be “Manual partitioning.”
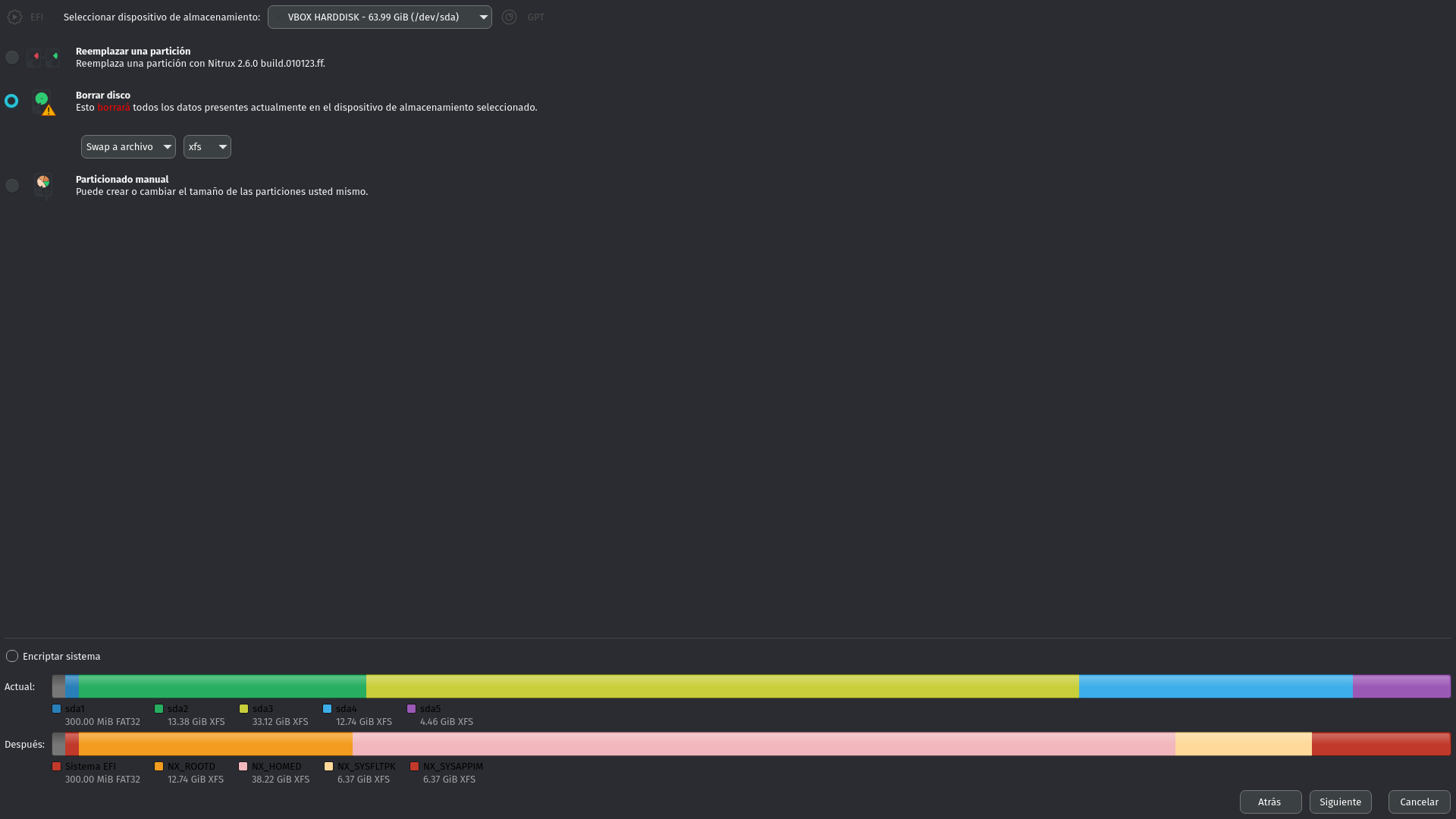
Our custom partition layout in Calamares.
-
-
- Do note that because of how Calamares works, it will allow you to select the option “Replace partition” if you have a partition with enough storage that meets the set size requirement, which will lead Calamares to attempt to create this partition layout inside the selected partition, instead of accommodating the partitions to the overall size of the storage device or allowing the selection of multiple partitions to replace. If it is the case that you want to replace multiple partitions, we strongly recommend using “Manual partitioning.”
- Calamares now adds custom kernel parameters to the GRUB file.
-
- We’ve added Pulseaudio Equalizer.
- Described as “A LADSPA-based multiband equalizer approach for getting better sound out of PulseAudio. This equalizer is more potent and easy to use than previous versions.”
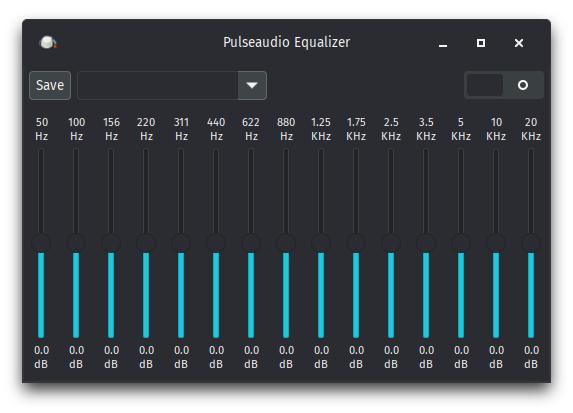
Pulseaudio Equalizer.
- We’ve updated the look of the default “Overview” of Plasma System Monitor to show the list of processes instead of applications, as the latter only works with systemd, and thus it does not work in Nitrux.

Updated Overview in System Monitor.
- We’ve added packages with debug symbols for the following software to help users send relevant bug reports to KDE.
- KWin
- Latte Dock
We’ve fixed or closed the following issues in the distribution; see Report bugs.
- Fixed the Calamares launcher on the desktop of the Live session so that it no longer triggers a warning when double-clicking it.
- Move to PipeWire #37.
- Touchpad gestures not working in Live session #32.
- Move to Wayland #20.
We’ve removed the following components from the distribution.
- dpkg, APT and PackageKit.
- Those with keen eyes might notice that we’re calling this version “ff,” but what does that mean? The “ff” stands for “forbidden fruit,” and it is the first time we use a codename to mark a distribution release. The peculiar choice of this codename is because, as is, this version of this distribution can be seen as the antithesis of the conventional Linux distribution, where a distribution is entirely devoted to its package manager, but this distribution is not. It works to drive the point home that in this distribution, AppImages are the preferred method of adding new applications, and where an AppImage is unavailable, having the option to use Flatpak.
- Admittedly, before marching down with torches in anger, be mindful that users can still use a package manager; in fact, users can use any package manager to install new software, just not directly to the root directory anymore. To do so, users can use Distrobox (check our tutorial) to create a container of absolutely any distribution available in DockerHub and very effortlessly use a package manager (we added Distrobox two months ago, complementing the inclusion of Docker two years ago); again, we can’t stress this enough.
- Those with keen eyes might notice that we’re calling this version “ff,” but what does that mean? The “ff” stands for “forbidden fruit,” and it is the first time we use a codename to mark a distribution release. The peculiar choice of this codename is because, as is, this version of this distribution can be seen as the antithesis of the conventional Linux distribution, where a distribution is entirely devoted to its package manager, but this distribution is not. It works to drive the point home that in this distribution, AppImages are the preferred method of adding new applications, and where an AppImage is unavailable, having the option to use Flatpak.
Users can use a container of any Linux distribution (Arch, Fedora, Debian, openSUSE, NixOS, Gentoo, and many more), including multiple containers simultaneously; there’s no limitation whatsoever. Distrobox also allows users to export software that uses a desktop launcher so that it’s automatically integrated into the application menu, even picking up the artwork from the host, like application themes and icons.
-
- Because Distrobox is considerably easy to use and intuitively transparent to the user, there are no plans to add any wrapper to use it.
- In addition to the highlights in What’s New, with this change, we can eliminate any shortcomings due to packages from upstream heavily relying on systemd components, like maintainer scripts using systemctl.
- To ensure it doesn’t go unnoticed, we added a help command to display a condensed version of the above.
- The Live ISO includes APT and dpkg, but this is because Calamares needs them to complete the installation and will be removed from the installed system.
- It’s worth mentioning that the Live ISO is intended to be used as installation media, rescue media, and an update method, see Notes.
- The Live ISO includes APT and dpkg, but this is because Calamares needs them to complete the installation and will be removed from the installed system.
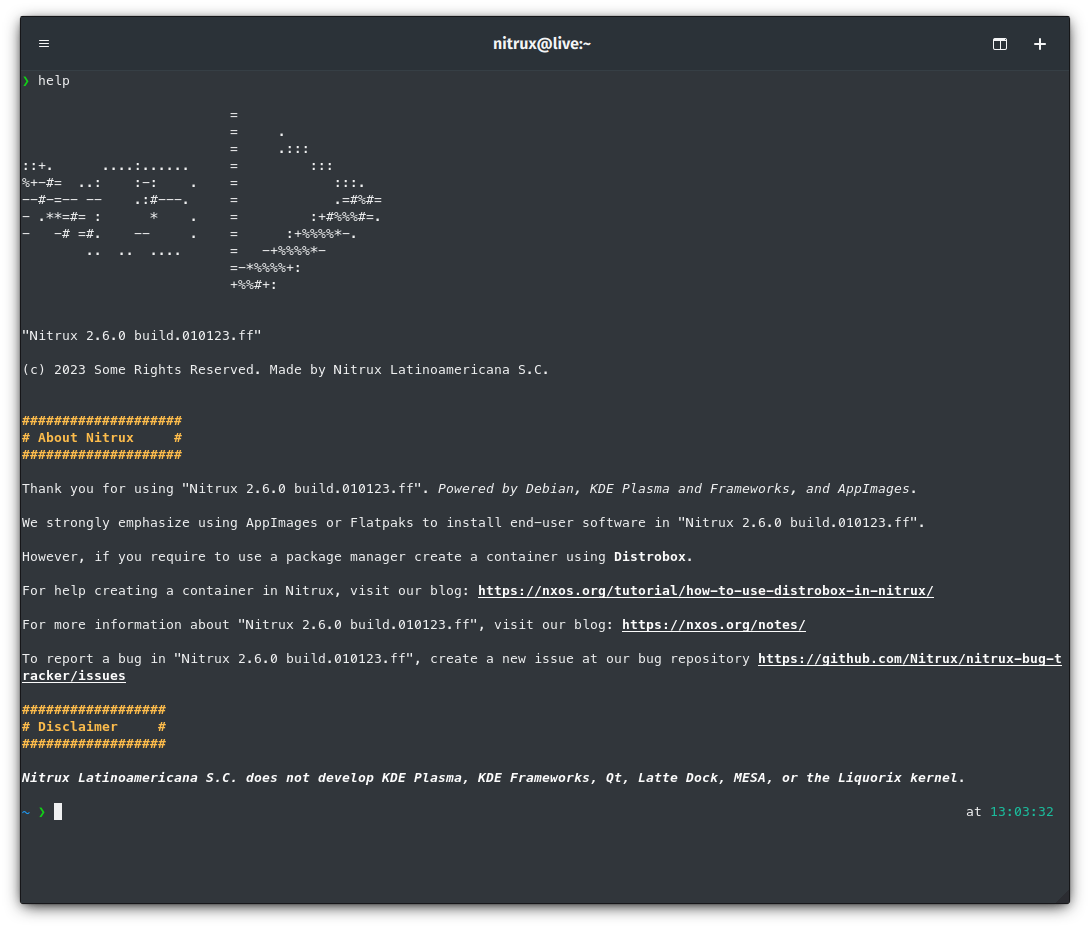
Typing ‘help’ in the terminal.
- Future releases of the minimal ISO with jwm are discontinued as it did not meet the expectations we had set for it; additionally, as we have mentioned in the past, it is also due to higher bandwidth cost.
- Again, before marching down with torches in anger, this change does not mean that users cannot install other desktop environments in Nitrux; please check our tutorial for an update.
📥 Download
Here are various ways to download our ISOs and virtual appliances.
- ISO — Direct HTTP Download from our server.
- FOSS Torrents (Torrent).
- Sourceforge (mirror).
- OSDN (mirror).
Checksums (MD5).
b6af21abeb11a493265fcd4b4d8524d7 nitrux-nx-desktop-d5c7cdff-amd64.iso
⛔ Known issues
To see a list of known issues, click here.
🗒 Notes
To see a list of release notes, click here.
🐞 Report bugs
To report bugs, please use our bug tracker on GitHub.
📝 Changelog history
To see a list of previous changelogs, click here for the changes archived at our site or for the changes archived at Sourceforge.
📰 Resources
Here are various articles, tutorials, and other information on our blog.
📌 Post-release announcements
Here’s a list of post-release service announcements for this version of Nitrux.